Logical data type in Power Query
In Power Query (M language), the Logical data type is used to represent Boolean values — basically true, and false.
Example: Filtering Rows.
Power Query M
let
// Step 1: Create a table with customer data including marks
source = Table.FromRecords(
{
[CustomerID = 1, Name = "Ashish", Marks = 568],
[CustomerID = 2, Name = "Katrina", Marks = 855],
[CustomerID = 3, Name = "Alia", Marks = 367],
[CustomerID = 4, Name = "Vicky", Marks = 458],
[CustomerID = 5, Name = "Mohini", Marks = 278],
[CustomerID = 6, Name = "Meenakshi", Marks = 289],
[CustomerID = 7, Name = "Esha", Marks = 875],
[CustomerID = 8, Name = "Anjali", Marks = 380]
}
),
// Step 2: Add a new column "Status" with logical value TRUE if Marks > 500
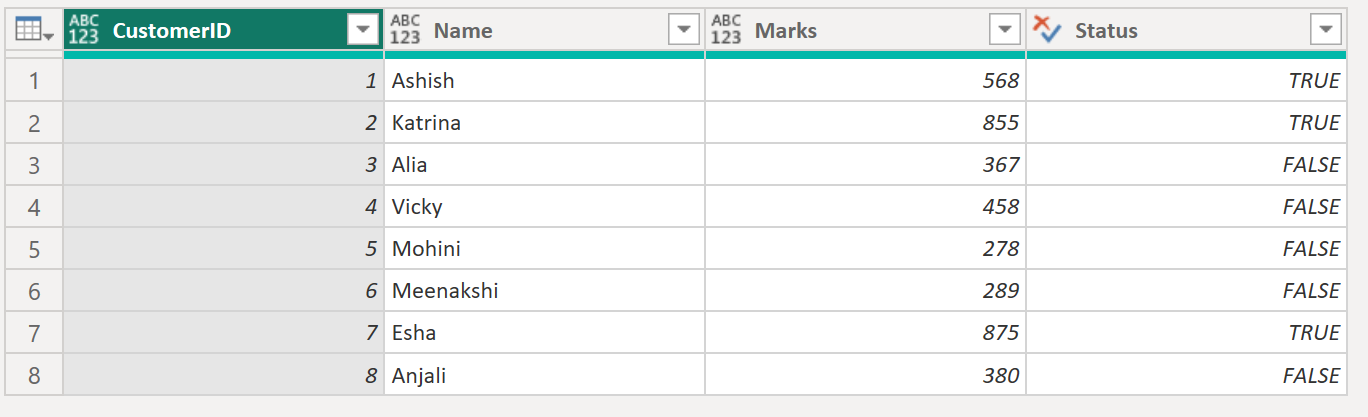
#"Add column" = Table.AddColumn(source, "Status", each [Marks] > 500, type logical),
// Step 3: Filter rows where "Status" is TRUE (i.e., Marks > 500)
#"Filtered Rows" = Table.SelectRows(#"Add column", each ([Status] = true))
in
// Output the filtered table
#"Filtered Rows" The output of the above code is shown below:
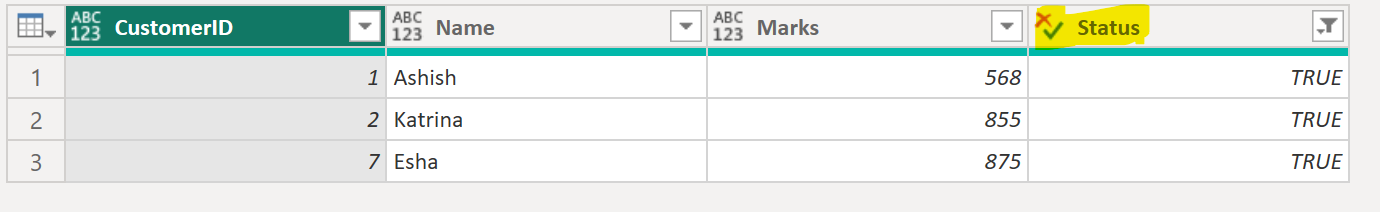
Example: Creating Conditional Columns.
Power Query M
let
source = Table.FromRecords(
{
[CustomerID = 1, Name = "Ashish", Marks = 568],
[CustomerID = 2, Name = "Katrina", Marks = 855],
[CustomerID = 3, Name = "Alia", Marks = 367],
[CustomerID = 4, Name = "Vicky", Marks = 458],
[CustomerID = 5, Name = "Mohini", Marks = 278],
[CustomerID = 6, Name = "Meenakshi", Marks = 289],
[CustomerID = 7, Name = "Esha", Marks = 875],
[CustomerID = 8, Name = "Anjali", Marks = 380]
}
),
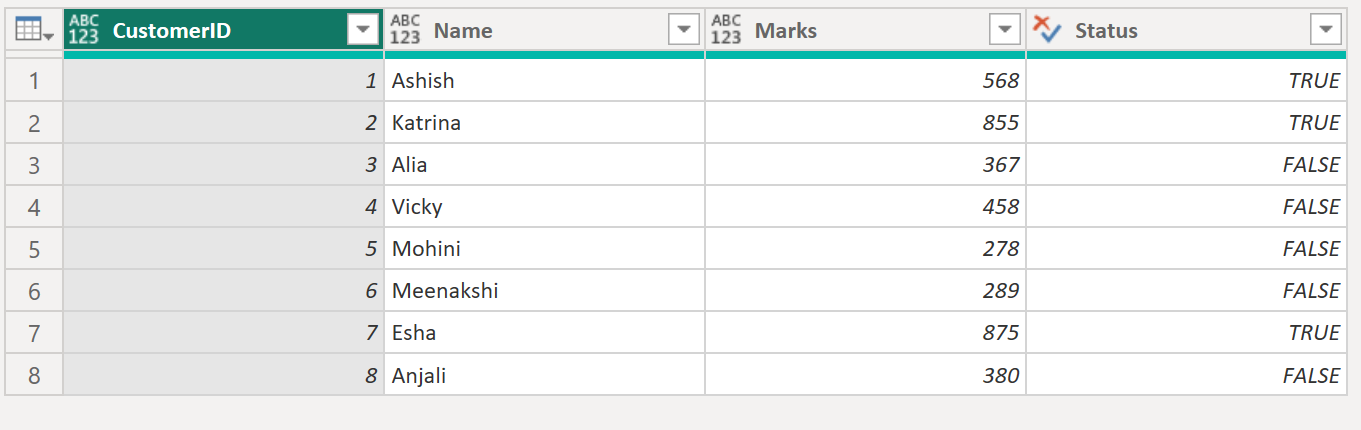
return = Table.AddColumn(source, "Status", each [Marks] > 500, type logical)
in
return This creates a new column of true or false values.
Example: Using in IF Statements.
Power Query M
let
source = Table.FromRecords(
{
[CustomerID = 1, Name = "Ashish", Marks = 568],
[CustomerID = 2, Name = "Katrina", Marks = 855],
[CustomerID = 3, Name = "Alia", Marks = 367],
[CustomerID = 4, Name = "Vicky", Marks = 458],
[CustomerID = 5, Name = "Mohini", Marks = 278],
[CustomerID = 6, Name = "Meenakshi", Marks = 289],
[CustomerID = 7, Name = "Esha", Marks = 875],
[CustomerID = 8, Name = "Anjali", Marks = 380]
}
),
return = Table.AddColumn(source, "Status", each if [Marks] > 500 then true else false , type logical)
in
return The output of the above code is shown below: